Understanding the lifecycle of requests in Laravel 11

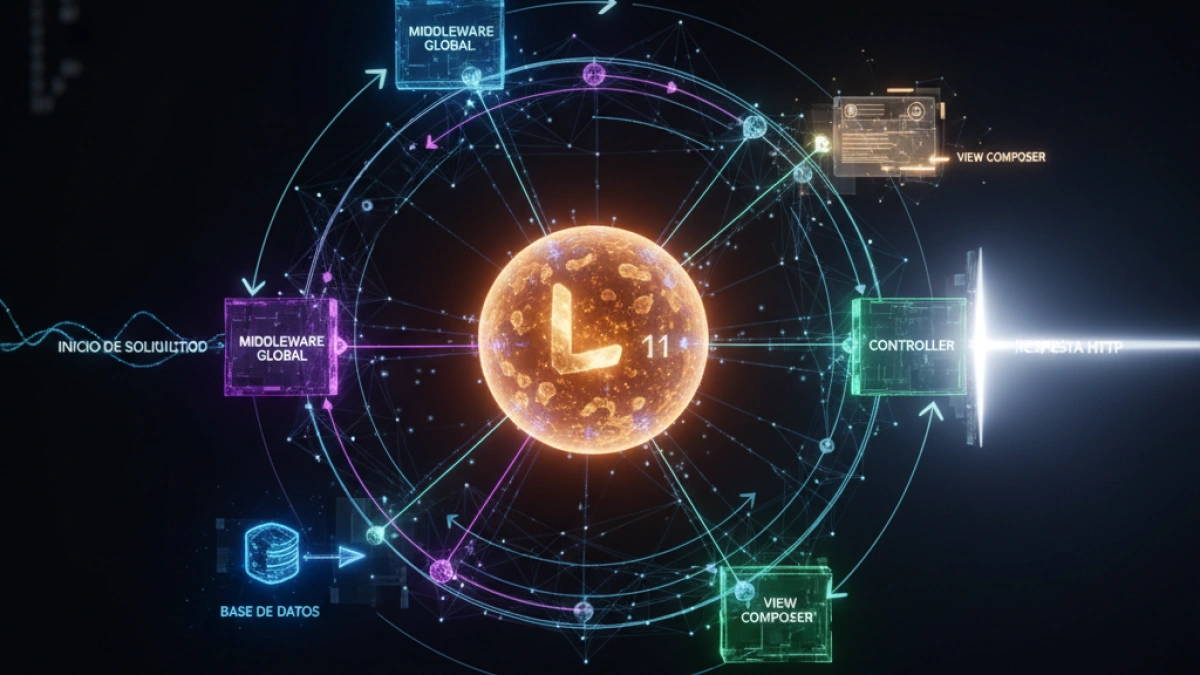
The Laravel framework has become an essential tool for many web developers, offering an elegant and efficient approach to creating applications. In its latest version, Laravel 11, improvements and a request lifecycle have been introduced that programmers must understand to optimize their applications. Below is the process that each request follows in Laravel 11.
What is the request lifecycle in Laravel?
The request lifecycle in Laravel refers to the series of steps that are executed from the moment a user submits a request until the server returns a response. Each of these steps is essential, as it determines how the data is handled and how user interactions are responded to.
1. Receiving the request
The first step of the lifecycle begins when Laravel receives a request through its public/index.php file. This file serves as the entry point for all incoming requests. Here, the framework loads the application environment and initializes the necessary components.
2. Middleware registration
Once the request is received, Laravel processes the middleware assigned to the application. Middleware are layers that allow code to be executed before or after the request is processed. For example, a middleware can check if the user is authenticated before granting access to a specific area of the application.
Read also
3. Request routing
After processing the middleware, Laravel evaluates the request to determine the corresponding route. Using the routing system, Laravel assigns the request to a specific controller or function that will handle that request. This is a crucial step, as it defines what business logic will be executed.
4. Controller execution
Once the route is determined, Laravel invokes the associated controller. The controller is a component that contains the logic necessary to process the request. Here, the developer can interact with models, perform database queries, and manipulate data as needed.
5. Response generation
After the controller has processed the request, a response is generated. This response can be in HTML, JSON, or any other type that is needed. The controller returns this response to the request lifecycle, which is finally prepared to be sent back to the client.
Read also
6. Output middleware
Before the final response is sent to the user, Laravel applies the relevant middleware once again. This stage allows for modifications to the response, such as adding HTTP headers, manipulating cookies, or logging information.
7. Sending the response
Finally, Laravel sends the response to the client. At this point, the request lifecycle is considered complete. The response is returned to the user's browser and is presented according to what the server has sent.
Conclusion
Understanding the request lifecycle in Laravel 11 is fundamental for all developers who use this framework. Each step of the cycle contributes to the final interaction between the server and the user, allowing for the development of more efficient and optimized applications.
I invite you to continue exploring more about Laravel and other web development topics on my blog, where you will find informative and useful articles. Don’t miss it!



















