How to implement MVC in PHP in a simple and effective way

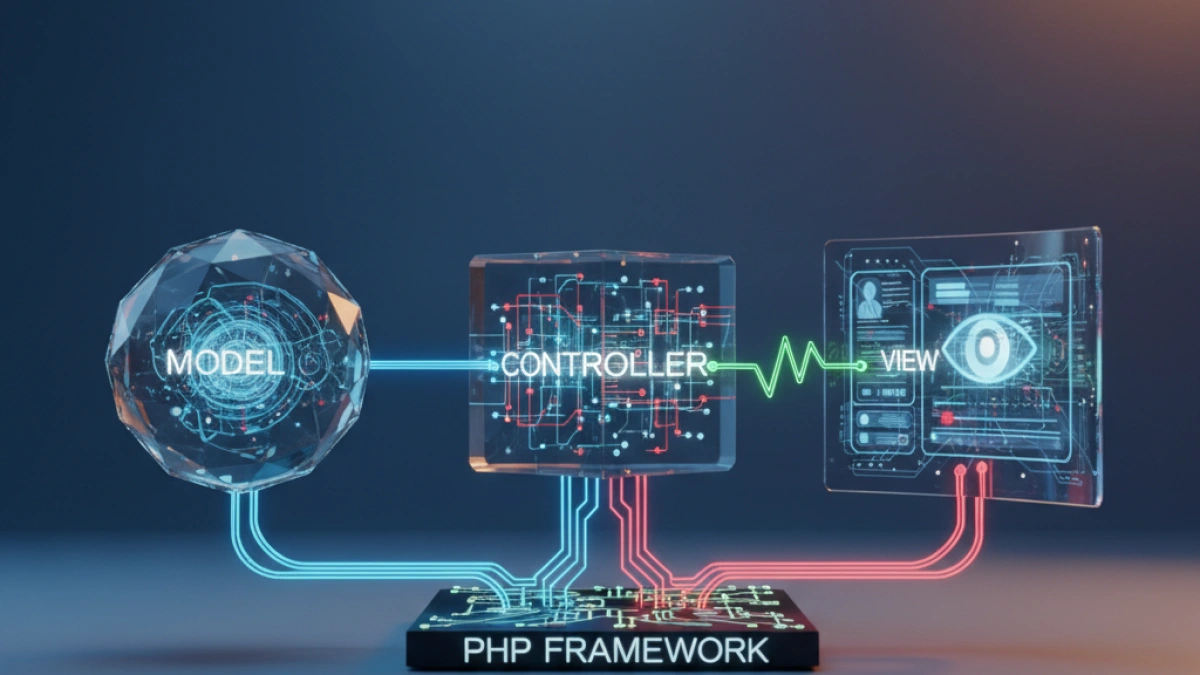
The Model-View-Controller (MVC) software architecture has become one of the most widely used frameworks for web application development. Its structure allows for the separation of concerns, making both the development and maintenance of code easier. In this article, I share a practical guide to implementing MVC in PHP in a simple and effective way.
What is MVC?
The MVC pattern organizes an application into three essential components:
-
Model: Manages data logic and interactions with the database. It defines the structure of the data and the operations that can be performed on it.
-
View: Responsible for presenting information. Everything the user sees and interacts with is contained in this layer.
-
Controller: Acts as an intermediary between the model and the view. It receives user requests through the view and decides which model to use to process the request before presenting the results back in the view.
Steps to Implement MVC in PHP
1. File Structure
To start, it is crucial to establish a clear folder structure. A typical structure would include:
/my_application
/app
/controllers
/models
/views
/public
index.php
/config
/vendor- app/controllers: Contains the application controllers.
- app/models: Here you'll find the models that manage data logic.
- app/views: Stores the views that will be shown to users.
- public: The public folder that hosts the
index.phpfile, where the application is initialized. - config: This folder contains the application configurations.
2. Create the index.php File
This file is the entry point of the application. It includes configurations and defines the routes. A basic example of index.php could be:
<?php
require '../config/config.php'; // Include configurations
// Initialize the controller
$controller = new Controller();
$controller->execute();
?>3. Define the Router
A router is essential to redirect requests to the appropriate controllers. This can be achieved using a routes file or directly in index.php. Here’s a brief example of how a simple router could be implemented:
$request = $_SERVER['REQUEST_URI'];
switch ($request) {
case '/':
$controller = new HomeController();
break;
case '/user':
$controller = new UserController();
break;
default:
http_response_code(404);
echo "404 Not Found";
exit;
}4. Create Controllers and Models
Controllers are responsible for receiving user input and calling the appropriate methods in models. For example, a user controller might look like this:
class UserController {
public function display() {
$model = new UserModel();
$data = $model->getUsers();
include '../app/views/users.php';
}
}As for models, they should contain methods that interact with the database and perform necessary operations, such as retrieving, creating, updating, or deleting data.
5. Build the Views
Finally, views are PHP files that handle displaying data to the user. For instance, a users.php file could contain a simple list of users.
<?php foreach ($data as $user): ?>
<p><?php echo $user['name']; ?></p>
<?php endforeach; ?>Conclusion
Implementing the MVC pattern in PHP provides a solid foundation for web application development, facilitating code scalability and maintenance. This pattern significantly reduces complexity, improving project organization.
If you would like to delve deeper into this topic and receive more content like this, I invite you to visit my blog. Stay tuned for the latest news in the world of web development!















